GROIN PAIN
Groin pain, referred to also as athletic pubalgia, is a common problem for a number of athletes, particularly those who engage in sports that require specific use (or overuse) of lower abdominal muscles and the proximal muscles of the thigh. Predominantly, these activities centre around kicking sports such as AFL and soccer, as well as long distance running. Ice hockey is also a well renowned sport in which chronic groin pain occurs. All these sports involve repetitive energetic kicking, twisting, turning or cutting movements, which are all risk factors for causing pubalgia.
SUMMARY:
- Four structures are commonly implicated in the causes of groin pain
- Adductor muscles
- Pubic bone
- Abdominal wall
- Iliopsoas
- Understanding which of these four structures is causing your pain is key in effective management
- Exercise therapy and activity modifications should be the mainstay of treatment
- Absolute rest has been shown to be ineffective
- Steady gradual progressions through strength and function, tailored to your goals, is key to successful management
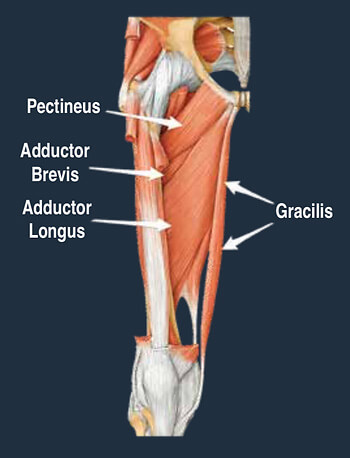
ROLE OF HIP ADDUCTORS (groin muscles)
Similar to other joints in the body, the hip relies on muscular control for stability and movement. At the hip, there are five key planes of movement; flexion, extension, abduction, adduction and rotation.
The adductor muscles are a large group of muscles located on the inner side of the thigh, attaching from below the knee, along the shaft of the femur and into the pubic bone of the pelvis.
While acute tears of the adductor muscle is common, more long standing pain is usually the result of an overload of the adductor tendon that attach to the pelvis. This is called an adductor tendinopathy. Adductor enthesopathy is common disorder which effects the bony attachment point of the tendon, with a slight structural difference from tendinopathy, however, management is similar in both cases
MANAGEMENT OPTIONS
Exercise:
Strength and functional based exercise are the core management strategies for adductor tendinopathy, and have been shown to increase function, decrease pain and reduce likelihood of injury [4].
Activity Modification:
Activity modification, especially in the acute phase or when symptoms are significantly affecting function, is key in reducing load on the affected structures and allowing tissues to adapt. [1]
Rest:
While activity modification is important, absolute rest has been shown to be ineffective in the management of adductor tendinopathy, and does not promote adequate tissue repair. [1,2]
Other:
Other conservative measures such as manual therapy, electrotherapy and stretching have been [1] explored, with reduced effect compared exercise prescription. Surgical management is also a potential option, with some positive results emerging for groin pain, though specific evidence [10] around adductor tendinopathy is limited. [10]
WHY IS EXERCISE IMPORTANT?
Exercise has been shown to increase tendon turnover, meaning in the first 24-36 hours there is a reduction in tendon integrity, but after that there is an overall increase in integrity and strength. Other benefits include: increased blood flow, increase in growth factors, and a reduction in altered pain processes in the brain [14].
WHAT’S THE BEST EXERCISE?
Isometric exercise has been shown to be effective in short term pain relief. Current evidence is unclear as to the best long term exercise strategies, with evidence supporting both eccentric and heavy-slow isotonic exercise. [12]
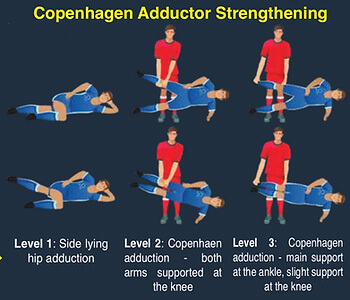
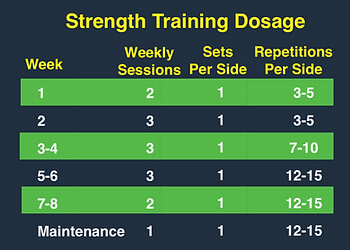
EXERCISE PLAN
The Copenhagen Adductor Program [9], with the below dosage, has been shown to significantly improve adductor strength, as well as being effective in groin injury prevention. It is important to note that though the program is eight weeks long, most effective tendon[12] adaptations take ≥ 12 weeks, and a tailored dosage should be discussed with your physiotherapist towards the end stage of rehabilitation.
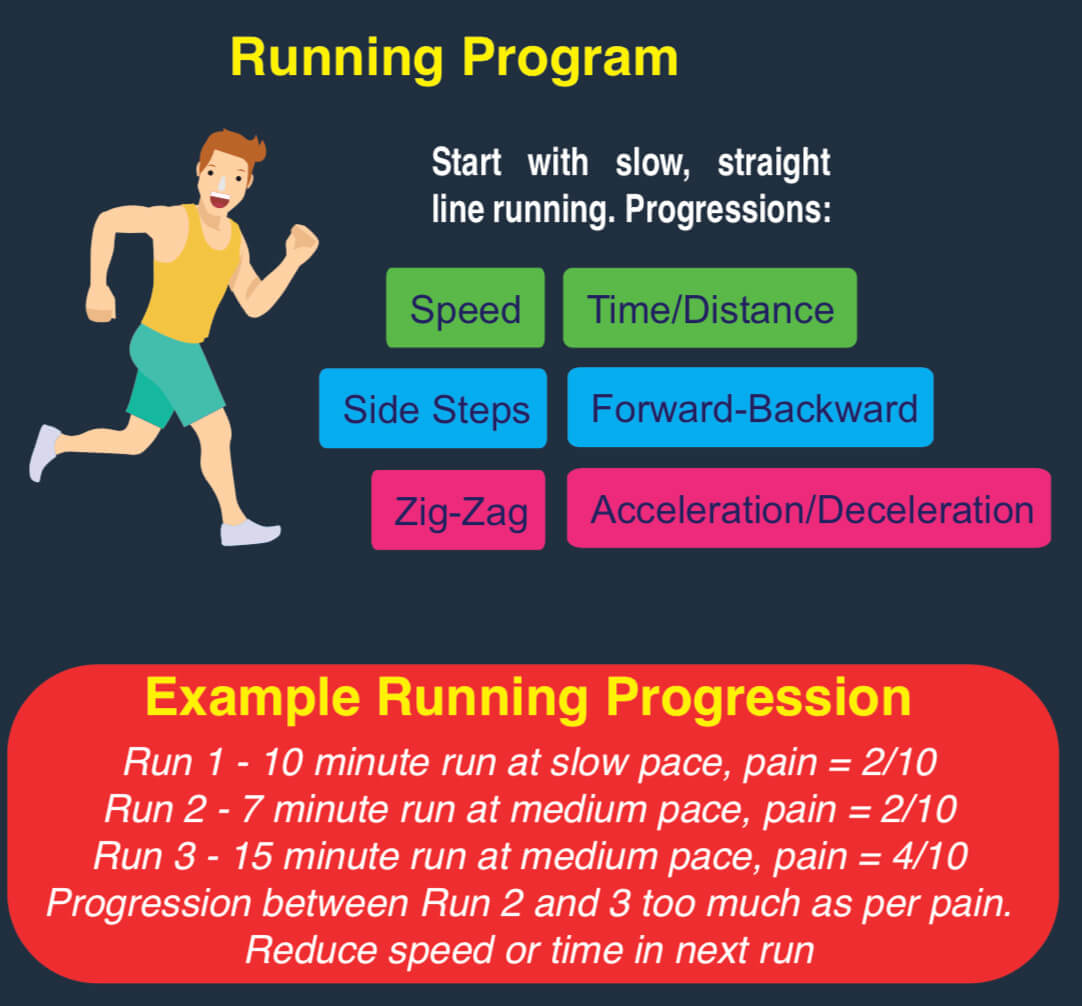
Depending on how the symptoms affect your function, a reduction in training, running and kicking may also be required. Example progressions are noted below in the running program, in order of loading on adductors.

ADDITIONAL STRENGTH AND PROGRAMS
While targeted strengthening to the adductors is key, global strengthening around the hip may also aid in a reduction of loading to the tendon. Thorough assessment of your strength through all five movements noted previously is needed, as well as a tailored training program to resolve any discrepancies.
As symptoms reduce and function improves, part practice of painful activities, can be beneficial to reload structures, for example, banded kicking movements in preparation for return to soccer.

SUMMARY
In chronic adductor tendinopathy, tendon adaptations take time. It is important to understand this as you begin your rehab journey and not progress more than your body can tolerate. Steady gradual progressions through strength and function, tailored to your goals, is key to successful management.
As always, if you have a history of groin pain or are concerned about performance in your chosen sport, contact us today and chat to one of our friendly and knowledgeable physiotherapist to ensure you can Prevent. Prepare. Perform. Alternatively you can book online here
Till next time, Praxis what you Preach
📍 Clinics in Teneriffe, Buranda, and Carseldine
💪 Trusted by athletes. Backed by evidence. Here for everyone.
References:
- Almeida, M.O., et al., Conservative interventions for treating exercise‐related musculotendinous, ligamentous and osseous groin pain. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2013(6).
- Bohm, S., F. Mersmann, and A. Arampatzis, Human tendon adaptation in response to mechanical loading: a systematic review and meta-analysis of exercise intervention studies on healthy adults. Sports Medicine – Open, 2015. 1(1): p. 7.
- Brukner, P., Brukner & Khan’s clinical sports medicine / Peter Brukner … [et al.]. Sports medicine series, ed. K. Khan. 2012, North Ryde, N.S.W: McGraw-Hill Australia.
- Charlton, P.C., et al., Exercise Interventions for the Prevention and Treatment of Groin Pain and Injury in Athletes: A Critical and Systematic Review. Sports Med, 2017. 47(10): p. 2011-2026.
- Frizziero, A., et al., The role of eccentric exercise in sport injuries rehabilitation. Br Med Bull, 2014. 110(1): p. 47-75.
- Griffin, V.C., T. Everett, and I.G. Horsley, A comparison of hip adduction to abduction strength ratios, in the dominant and non-dominant limb, of elite academy football players. Journal of Biomedical Engineering and Informatics, 2015. 2(1): p. 109.
- Haroy, J., et al., The Adductor Strengthening Programme prevents groin problems among male football players: a cluster-randomised controlled trial. Br J Sports Med, 2019. 53(3): p. 150-157.
- Harøy, J., et al., Infographic. The Adductor Strengthening Programme prevents groin problems among male football players. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 2019. 53(1): p. 45.
- Haroy, J., et al., Including the Copenhagen Adduction Exercise in the FIFA 11+ Provides Missing Eccentric Hip Adduction Strength Effect in Male Soccer Players: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am J Sports Med, 2017. 45(13): p. 3052-3059.
- Jorgensen, S.G., S. Oberg, and J. Rosenberg, Treatment of longstanding groin pain: a systematic review. Hernia, 2019.
- Kohavi, B., et al., Effectiveness of Field-Based Resistance Training Protocols on Hip Muscle Strength Among Young Elite Football Players. Clin J Sport Med, 2018.
- Lim, H.Y. and S.H. Wong, Effects of isometric, eccentric, or heavy slow resistance exercises on pain and function in individuals with patellar tendinopathy: A systematic review. Physiother Res Int, 2018. 23(4): p. e1721.
- Machotka, Z., S. Kumar, and L.G. Perraton, A systematic review of the literature on the effectiveness of exercise therapy for groin pain in athletes. Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Ther Technol, 2009. 1(1): p. 5.
- Magnusson, S.P., H. Langberg, and M. Kjaer, The pathogenesis of tendinopathy: balancing the response to loading. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2010. 6(5): p. 262-8.
- Rio, E., et al., Tendon neuroplastic training: changing the way we think about tendon rehabilitation: a narrative review. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 2016. 50(4): p. 209.
- Thorborg, K., et al., The Copenhagen Hip and Groin Outcome Score (HAGOS): development and validation according to the COSMIN checklist. Br J Sports Med, 2011. 45(6): p. 478-91.
- Wei, A.S., et al., The effect of corticosteroid on collagen expression in injured rotator cuff tendon. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume, 2006. 88(6): p. 1331-1338.

