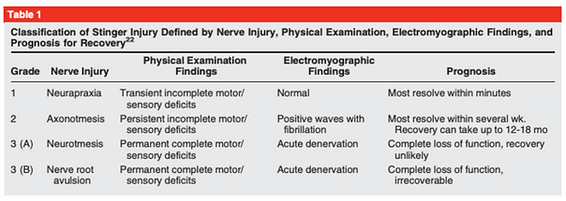
Knee Pain
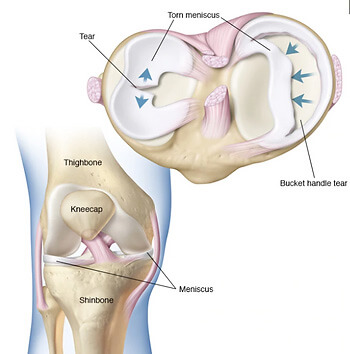
Different knee injuries tend to have differing symptoms. Common symptoms include:
- Aching, sharp, stabbing and/or catching pains
- Large amounts of swelling or sometimes pockets of swelling
- Warm to touch
- Feelings of grating, grinding or even giving way
- Pops and crunching noises
- Unable to full bend or straighten the knee
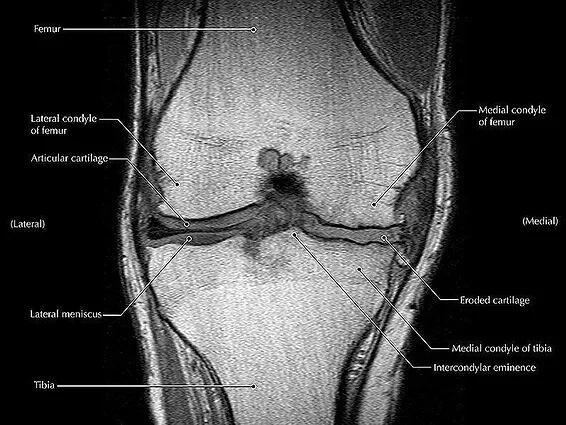
The structures of the knee that are often implicated in knee pain are the patellar or quadriceps tendons, cartilage, meniscus, bursas, and even major ligaments such as the anterior cruciate ligament, otherwise known as the ACL.
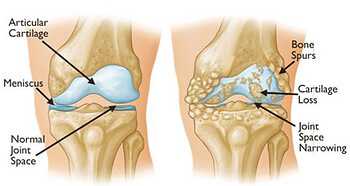
Common injuries to the knee can be:
- Osteoarthritis
- Tendinopathy / Tendonitis
- Bursitis
- Knee cap pain (patellofemoral pain)
- Meniscal tear (degenerative and acute tears)
- Dislocated knee cap
- Iliotibial band friction syndrome
Regardless of your symptoms and presentation, our highly trained Praxis physiotherapists have expertise in this area and will help identify the problem and work with you so that you will feel empowered to fix the problem. At Praxis Physio this is our point of difference, we promise to take the time to fix you using a range of modalities including advice, hands on manual therapies and of course strength and conditioning programming. In addition, we work in close collaboration with leading knee surgeons if this course of action is required.

There is no need to accept knee pain as ‘normal’. Call us now on (07) 3102 3337 or book online to have one of our physios develop a plan to reduce your pain and restore your function!
To read more about how running can help your knees (that’s right – running!) check out our related posts on running written by our published principal physio, Stephen.
Team Praxis,
PREVENT | PREPARE | PERFORM