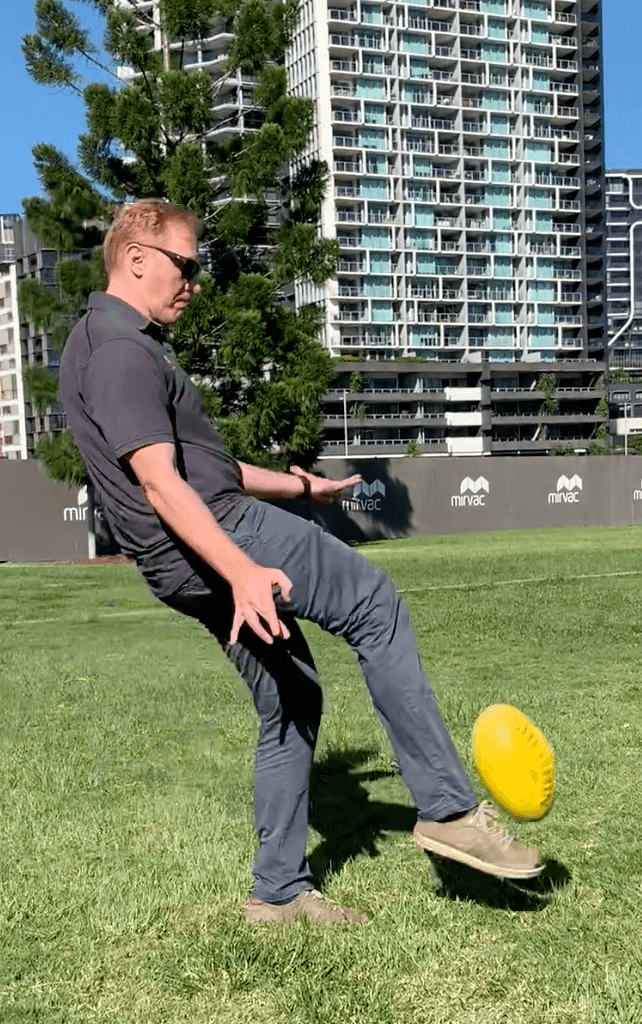
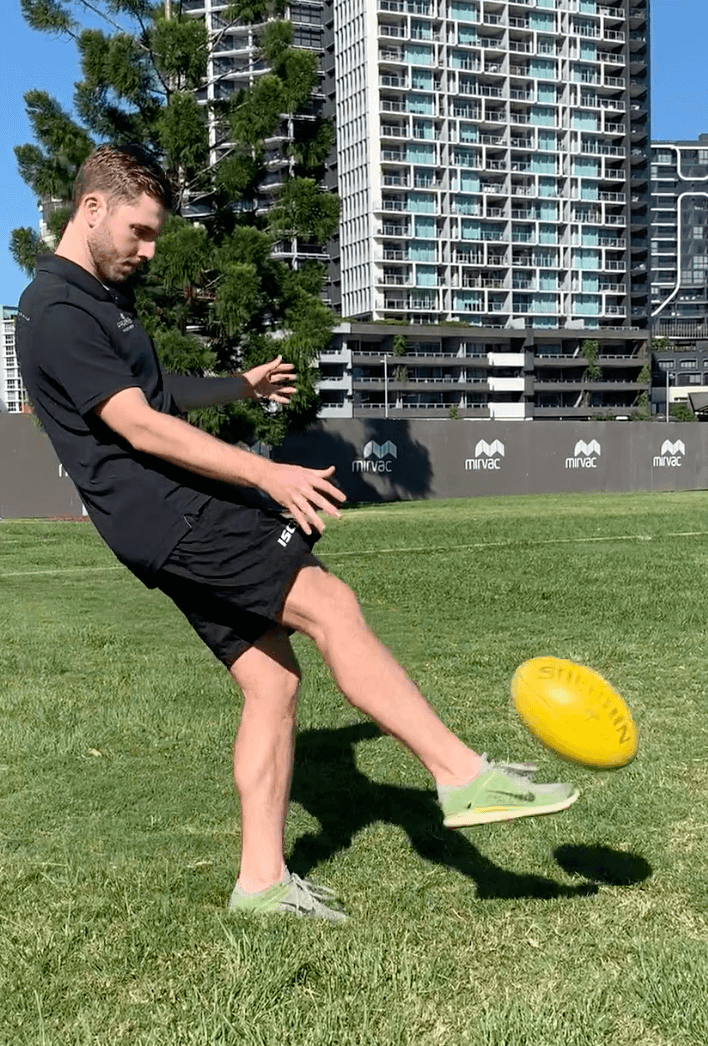
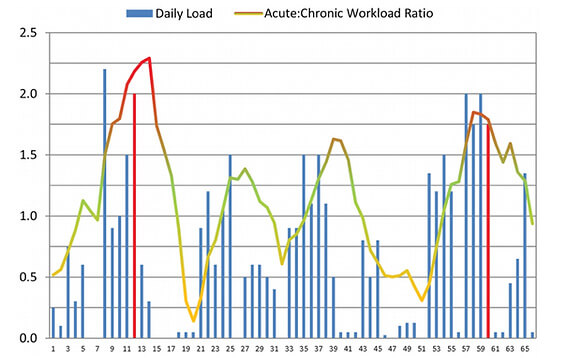
ROLE OF HIP ADDUCTORS (groin muscles)
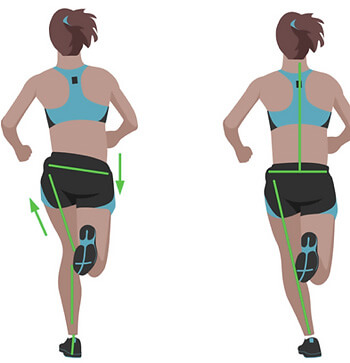
Similar to other joints in the body, the hip relies on muscular control for stability and movement. At the hip, there are five key planes of movement; flexion, extension, abduction, adduction and rotation.
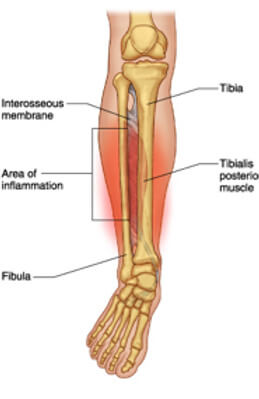
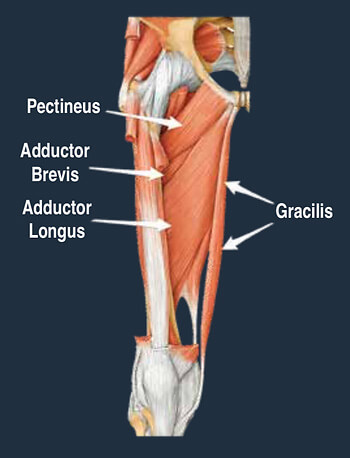
The adductor muscles are a large group of muscles located on the inner side of the thigh, attaching from below the knee, along the shaft of the femur and into the pubic bone of the pelvis.
While acute tears of the adductor muscle is common, more long standing pain is usually the result of an overload of the adductor tendon that attach to the pelvis. This is called an adductor tendinopathy. Adductor enthesopathy is common disorder which effects the bony attachment point of the tendon, with a slight structural difference from tendinopathy, however, management is similar in both cases
MANAGEMENT OPTIONS
Exercise:
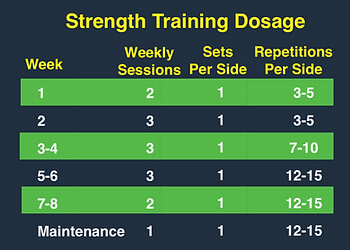
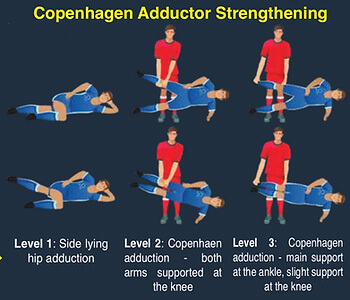
Strength and functional based exercise are the core management strategies for adductor tendinopathy, and have been shown to increase function, decrease pain and reduce likelihood of injury [4].
Activity Modification:
Activity modification, especially in the acute phase or when symptoms are significantly affecting function, is key in reducing load on the affected structures and allowing tissues to adapt. [1]
Rest:
While activity modification is important, absolute rest has been shown to be ineffective in the management of adductor tendinopathy, and does not promote adequate tissue repair. [1,2]
Other:
Other conservative measures such as manual therapy, electrotherapy and stretching have been [1] explored, with reduced effect compared exercise prescription. Surgical management is also a potential option, with some positive results emerging for groin pain, though specific evidence [10] around adductor tendinopathy is limited. [10]